Proxy vs. VPN – What is the Difference?
- By Douglas Moore
- January 30, 2024
Disclosure: Some links in this guide are affiliate links. We may get paid if you buy something or take an action after clicking one of these links, at no additional cost to you. It’s how we fund the work that it takes for us to create and maintain these guides.

This article will introduce the concept of proxies and VPNs, as well as their advantages and disadvantages, in hopes of helping you make a smart decision for your needs.
What Is a Proxy and How Does It Work?
A proxy serves as a go-between for you and the internet. When you utilize a proxy server, your online activity is channeled through that server prior to arriving at the intended website. As a result, the proxy can view and log all the websites you access and any data you enter, such as login credentials and payment details.
Web-based proxies and VPNs are both tools for enhancing online privacy, but they function differently. Web-based proxies act as an intermediary for a single web application, like a browser, allowing you to browse anonymously for that specific session. However, they typically don’t encrypt your data, offering a lower security level than VPNs.
Using a web-based proxy allows you to browse the internet with a degree of anonymity, as the websites you visit will only see the proxy server’s IP address and not your own. However, it’s important to note that web-based proxies generally only secure the traffic going through your web browser while connected to the proxy.
Advantages of Using a Proxy
There are several advantages to using a proxy server.
- Anonymity: When you connect to a proxy server, your IP address is hidden from the sites you visit. This means that your identity and location are not revealed to anyone who might be monitoring or controlling your internet activity.
- Security: Proxy servers encrypt your traffic before it reaches its destination, making it more difficult for hackers to attack, intercept, or eavesdrop on your communications.
- Accessibility: Proxy servers can access websites blocked in your country or region.
- Flexibility: You can use a different proxy server for each internet connection, which gives you greater control over which sites are accessible and which aren’t.
Disadvantages of Using a Proxy
While proxy servers offer many advantages, they also have disadvantages.
- Slower speeds: Because Proxy servers route your traffic through an intermediary, there is inevitably some loss of speed. This can be especially noticeable with video streaming or gaming, where real-time communication is essential.
- Fragmented compatibility: Some website features may not work when accessed through a proxy server.
What is a VPN, and How Does It Work?
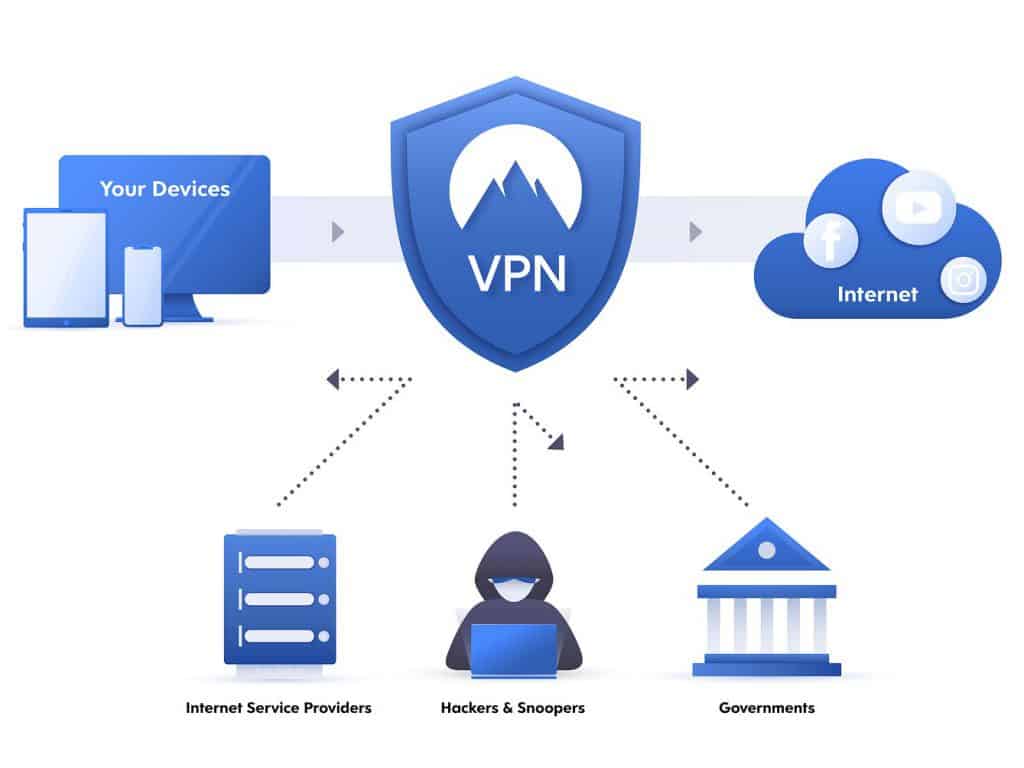
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a private network that can encrypt and channel internet traffic through public servers to mask the user’s identity and location. You can use VPNs for various purposes, including online privacy, security, and unblocking websites.
When a user connects to a VPN server, their traffic is first encrypted by the VPN server before it’s sent to the internet. This encryption makes it difficult to snoop on users’ traffic or track their online activity. Additionally, because the user’s traffic is routed through the VPN server, their true IP address is hidden from any websites they visit. This allows users to browse the internet anonymously, avoid marketing trackers, and access blocked content.
There are several different ways to set up a VPN, but most involve installing software on your device and connecting to a server run by the VPN provider. Once you’re connected, all your traffic will be routed through the VPN server before it reaches the internet. This gives you an extra layer of security as well as anonymity.
Many different types of VPNs are available today, each with its own features and benefits. Some common features include:
- Encryption: As mentioned above, all data passing through the VPN server is encrypted to protect users’ privacy.
- Protocols: Several different protocols are available, each with advantages and disadvantages. The most common protocols are PPTP, L2TP/IPSec, SSTP, IKEv2/IPSec, and OpenVPN.
- Speed: The connection speed of different VPN servers depends on which protocol you use, as well as other factors like congestion on the network.
- Logging Policy: Some VPN providers keep logs of user activity, while others do not log anything for maximum privacy protection. It’s essential to check what kind of logging policy each provider has before signing up for one.
Advantages of Using a VPN
So, what are the reasons for choosing a VPN? Let’s review the main benefits.
- Privacy Protection: Similarly to web-based proxies, the main advantage of using a VPN is that it helps protect your privacy by encrypting your traffic and hiding your real IP address. This makes it much more difficult for anyone to track your online activities or spy on your communications.
- Security: Besides privacy protection, using a VPN provides security benefits by encrypting your traffic. This makes it much less likely that hackers will intercept or steal your data when you’re using public Wi-Fi or other insecure networks. Additionally, some businesses require employees to use a corporate VPN to access sensitive company information while working remotely.
- Unblock Websites: Another common reason people use VPNs is to unblock websites that are censored in their country. By connecting to a VPN server in another country, you can bypass government censorship and gain access to newspapers, social media sites, and other blocked content. Additionally, some streaming services like Netflix use tight geo-restrictions to prevent users from accessing content unavailable in their country. However, you can often get around these restrictions by connecting to a VPN Server in another country where the content is available.
Disadvantages of Using a VPN
Just like web-based proxies, VPNs have some cons, too.
- Connection speeds can suffer: Because your data must travel through the VPN service before reaching its final destination on the network’s website that you’re trying to access, this can often result in slower connection speeds. Videos usually take longer to load, which can also impact your gaming performance.
- Limited server selection may impact accessibility in certain regions: Not every VPN service offers servers in every part of the world. So, if you wanted to connect to nearby servers located in another country to protect yourself from government surveillance or bypass regional internet censorship, it might not be possible.
- You still may be tracked by Your ISP(Internet Service Provider): Even though all data passing through a VPN is encrypted, third parties may still access your metadata, which tells them what type of sites and services you’ve been connecting to as well as timestamps. The metadata doesn’t reveal your name, so these third parties would still need to get a hold of a court order to view individual subscriber data, but it’s something to keep in mind.
Proxy vs VPN: Which Is Better for Online Privacy?
Let’s examine some key considerations when choosing between a Proxy and a VPN.
- The level of security offered by the proxy or VPN. A proxy offers basic security, while a VPN offers more robust security features.
- The level of anonymity provided by the proxy or VPN. A proxy may not offer complete anonymity, while a VPN can offer more anonymity by encrypting your traffic.
- The speed of the proxy or VPN. A proxy may be faster than a VPN, but a VPN can offer better speeds by bypassing geo-restrictions.
- The price of the proxy or VPN. A proxy is often cheaper than a VPN, but a premium VPN can offer better value for money with its features and support.
A Few Words Before You Go
When it comes to online privacy, both proxies and VPNs can be effective tools. However, some key differences between the two should be taken into account when making a decision about which one to use.
Proxies act as an intermediary between your computer and the internet, routing your traffic through a different server and hiding your IP address. This can provide some anonymity and privacy, but it does not encrypt your traffic, meaning that your data could still be intercepted by third parties. Additionally, proxies can sometimes be slow and unreliable.
VPNs, on the other hand, encrypt all of your traffic before it leaves your device. This provides a higher level of security and privacy, but it can also slow down your connection speed.
When choosing between a proxy and a VPN, it’s important to consider what level of security and privacy you need, as well as how much you’re willing to sacrifice in terms of speed and convenience.
View Related Articles
What Does a VPN Hide?
But what exactly does a VPN hide? There’s a bit of confusion over this question, so we’ll go over each type of data that a VPN helps you keep private. Keep in mind that this is only true of quality, paid VPN providers.

How to Watch BBC iPlayer Outside the UK
The best way to watch BBC iPlayer outside the UK is by using a VPN. Once you connect your PC, smartphone, or iPad (i.e. tablet) to the VPN, you’ll be able to connect to a UK server and directly access content. In this article, show you how you can use a VPN to watch BBC iPlayer from anywhere in the world.
Fast or Slow, Everything You Wanted to Know About VPN Speed
There’re a lot of things a VPN can do for you. It can add a layer of security against online threats, it can help you keep your data private from third parties, and it can help you access geo-blocked content worldwide, like some geo-restricted streaming services.
